ArrayAccess 接口
平常使用的 Laravel 框架的模型对象既可以使用箭头来进行赋值, 又可以使用数组方式进行赋值.
1 | <?php |
通过以上两种方式都能给对象赋值, 这个功能主要是实现了 ArrayAccess 接口和 __get 和 __set 这两个魔术方法.
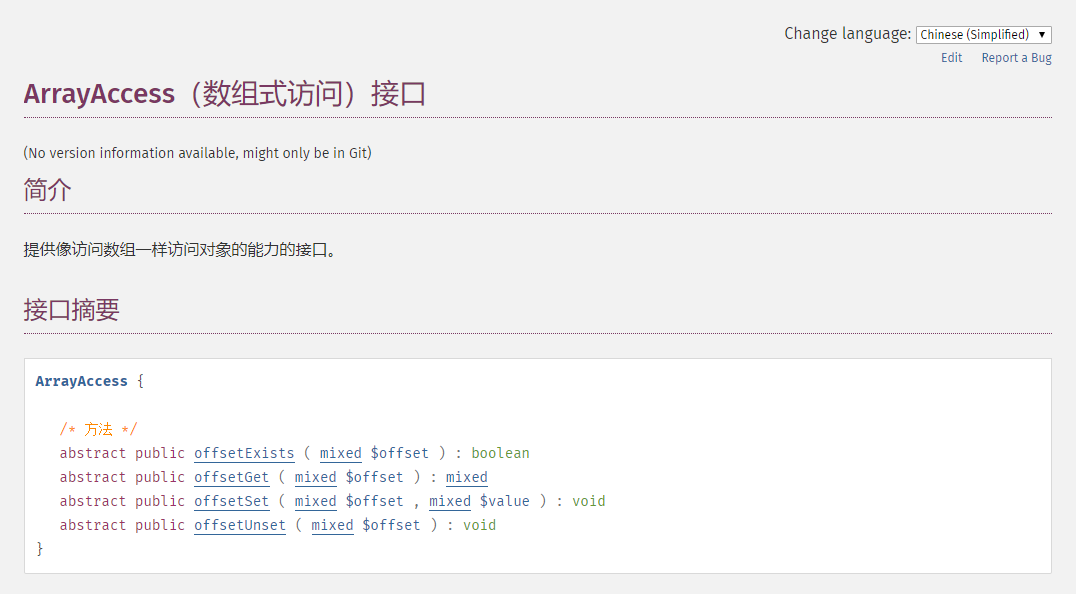
实现 ArrayAccess 接口需要实现四个方法.
offsetExists(mixed $offset): boolean: 检查一个偏移位置是否存在offsetGet(mixed $offset): mixed: 获取一个偏移位置的值offsetSet(mixed $offset, mixed $value): void: 设置一个偏移位置的值offsetUnset(mixed $offset): 复位一个偏移位置的值
其中
$offset参数代表数组的键,$value参数代表数组的值
实现 ArrayAccess 接口
1 | <?php |
执行结果1
2RandyChan
M17607475471@163.com